All organizations face risks of some variety. For financial institutions, the threat of money laundering and data breaches can have a fundamental impact on growth, legal compliance, and customer or stakeholder trust. With so much on the line, it’s perhaps no surprise that as many as 75% of banks are now investing in risk technology transformation in order to heighten their existing risk assessment and monitoring protocols.
The global risk management industry was estimated to be valued at $14.9bn in 2024, with projections suggesting this figure is set to rise as we head into 2026 and beyond. As such, it’s never been more important to have a robust and thorough risk monitoring policy in place to stay on top of any potential threats. Read on to discover more about the importance of risk monitoring, as well as what can be done to ensure your organization is keeping itself protected.
What is risk monitoring?
Risk monitoring is the continued process of assessing an organization's risk environment, risk management program, and associated activities to support risk decisions. It is a core component of determining how much risk an institution can tolerate, and is commonly used to create Key Risk Indicators (KRIs).
The risk monitoring process involves continuously evaluating financial risks, monitoring risk mitigation efforts, and ensuring that risks remain within acceptable pre-determined metrics. This helps organizations make proactive decisions about financial assets, while helping to support wider financial health.
What are the methods of risk monitoring?
Several methods can be employed to ensure that risk monitoring is carried out effectively. These help to detect, assess, and manage any potential threats. Some of the most common methods of risk monitoring are:
Audits and assessments
These are crucial for assessing the effectiveness of existing risk management systems, as well as helping to identify any new potential risks. These kinds of audits can either be scheduled periodically (this is generally considered best practice) or triggered by a specific event which might prompt you to assess existing risk monitoring framework.
Continuous monitoring
It’s important to employ a policy of continuous monitoring of real-time data from a number of sources within your organization. This allows for immediate intervention, as threats can be flagged proactively, as they occur.
Scenario analysis and stress testing
It’s now possible to automate and simulate risk scenarios to determine the impact they might have on an enterprise. These help to highlight potential vulnerabilities within a system, making it possible to prepare and mitigate the impact of adverse future events.
These specific types of assessment are carried out to help identify and evaluate the potential risk of fraud within an organization. They look to detect fraudulent activity and potential weak spots in your existing risk management framework via the analysis of process, controls, and transactions.
Incident reporting
A good risk monitoring system is reliant on the effective reporting of any incidents or issues. These occurrences need to be documented to ensure that the incidents in question are captured and analyzed properly. In turn, this helps to patch any issues with the existing risk management framework, while also helping to prevent future issues.
Risk indicators and metrics
KRIs and other metrics help to quantify and track the level of risk an organization is willing to tolerate. They both highlight early warning signals and help to measure the effectiveness of existing risk management strategies.
The importance of risk monitoring
Risk monitoring plays a vital role in the ongoing assessment, understanding, and mitigation of an organization’s financial risks. The impact of this can be felt across a variety of influential aspects of wider business management. This includes areas such as:
Risk safeguarding
Having an ever-present and defensive platform which monitors and manages risks helps to prevent issues from occurring. While it’s impossible to guarantee that all risks will be blocked at source, implementing risk monitoring techniques means that a high percentage are caught and addressed as early as possible.
Impact mitigation
Monitoring helps to reduce the impact that potential risks might have. It makes it possible to take swift and measured action as soon as a risk is identified – mitigating its potential long term impact, or even preventing a risk from having any kind of impact at all if it’s caught early enough.
Transparency fosters trust
Employees, stakeholders and customers are all going to develop a heightened level of trust in any organization that can accurately and transparently highlight where they’ve both detected and mitigated the impact of a potential risk. This transparency can also promote learning opportunities.
Growth support
At its core, risk monitoring ensures that wider growth is supported. By minimizing the losses associated with the risk which are being monitored, an organization is able to push forward and focus on expanding.
Comprehensive view
Risk monitoring also provides a rounded and comprehensive view of the wider risk landscape. This gives an enterprise the power heading forwards to act proactively, rather than reactively. The more data that’s collected, analyzed and accurately reported on, the easier it is to understand where potential future issues might arise from, as well as how to deal with them.
What are the different types of risk monitoring?
Risk monitoring can be carried out in a range of forms. These vary depending on the needs and legal requirements associated with the organization in question. The three main types of risk monitoring are:
Voluntary risk monitoring
This is the term used when organizations actively decide to monitor potential risks purely to avoid negative business outcomes. It’s common to analyze historical data in order to create future risk management practices which help a company grow and learn how to better protect themselves.
Obligated or mandatory risk monitoring
In industries or sectors where compliance with specific laws and standards is mandatory, obligated risk monitoring will need to be carried out. This usually applies to financial enterprises or even healthcare providers, who collect and store sensitive personal information for their customers. These kinds of monitoring setups require the close following of enforced legal regulations and processes. Failing to do so can result in legal penalties.
Continuous risk monitoring
This approach sees the ongoing use of real-time data to ensure that risks are being tracked effectively and accurately. This constant vigilance helps organizations to adapt quickly and prevents potential issues. The use of automated alerts, continuous control testing, risk impact scoring, and comprehensive risk reporting are all facets of continuous risk monitoring. This kind of monitoring is emerging as arguably the most important, as it provides an ongoing assessment of risk at a time when a dynamic threat landscape is making it harder than ever to keep private information safe.
How does risk monitoring apply to the banking industry?
Introducing a Customer 360 can have a transformative benefit to customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and wider profitability. Here are some of the biggest benefits which you’ll experience by implementing one:
The banking industry is particularly susceptible to fraud, owing to the vast amount of money intrinsically associated with the sector. Anti-money laundering (AML) is a good example of how risk monitoring is carried out within the industry. These kinds of tools and approaches might handle the monitoring of potential financial risks in the following ways:
Customer risk assessments help to prioritize and manage client risk. Monitoring here is designed to help a bank understand how a launderer might be able to exploit their products or services. These assessments also help ensure compliance with existing regulations.
Banks also need to follow strict compliance with existing government regulations. Failing to do so can result in hefty fines, legal challenges, and damage to an organization’s professional reputation.
A compliance team can be created to ensure that the correct procedures are being followed in regards to the ongoing monitoring and management of risk. This is both in accordance with internal processes, as well as government enforced procedures.
AML software helps to support the continuous and real-time monitoring of risks. This system should provide detailed information, such as users with suspicious activity associated with their accounts.
How does risk monitoring fit into a risk management process?
Risk monitoring is a crucial aspect of any risk management process. In total, the banking risk management process contains six different core components. Let’s now take a closer look at all of them, as well as where risk monitoring fits into the picture:
Identification
The process begins by working out the nature of the risk. This means establishing where it’s originating from and exactly why it poses a threat.
Assessment and analysis
All risks are then assessed for their level of threat. This helps to prioritize which issue needs to be addressed first in order to mitigate potential losses.
Mitigation
Part of this mitigation process is creating and defining policies which limit and minimize the threat that a risk might cause. Having these systems in place makes it possible to understand how much impact a risk may or may not have.
Monitoring
The focus of this guide. Monitoring gathers data on threat prevention and incident response to assess how well an existing risk prevention strategy is working. This might also involve researching existing risk trends to determine if a risk management framework needs to be updated.
Cooperation
A centralized and coordinated threat response system helps to keep an organization even safer. This needs to involve an amalgamation of enterprise risks and mitigation strategies across different areas of the business.
Reporting
Documenting and ongoing reporting are crucial for helping to gauge the success of all the efforts from the previous stages. This will also help to provide an accurate overview of the risk profile of specific accounts and the wider risk management strategy.
As you can see, risk monitoring is just one piece of the wider risk management process. Each of these factors needs to be carried out in unison in order for an organization to get the most thorough and efficient level of protection. Risk monitoring in particular helps to enhance the risk management process in the following ways:
Early threat detection
Heightened preparedness and response times
Compliance with government regulations
Streamlined and informed decision-making
Helping to create a risk-aware internal culture
Efficient and focused resource allocation
Facilitating growth and development
Improving stakeholder and customer confidence
Effective risk monitoring tools
The successful monitoring and management of potential risks relies on the implementation of tools created to detect, assess, and manage threats. Understanding what kinds of tools can be employed will make it easier to know if your organization is doing what it can to remain safe.
These tools are able to track, analyse and report on risks before they can have an impact. As standard, these kinds of systems usually leverage dynamic elements such as risk assessment, incident management, and compliance tracking.
The purpose of these scanners is to scan and assess any potential flaws or vulnerabilities in an organization’s systems or applications. Finding and isolating these points of weakness provide the opportunity to promptly address them, reducing the greater threat posed by any such flaw.
These systems collect and analyze data in real-time from a variety of security-related sources. This gives a holistic overview of an organizations’ overall security procedures, making it easier to identify and respond to major threats more quickly.
These platforms look at multiple sources to calculate the possibility of emerging threats and potential attack vectors. They in essence serve as research into the latest threats to watch for, making it easier to stay on top of the latest risks in the sector.
Machine learning can be used to identify any suspicious activity which appears fraudulent in any way. These systems are able to flag potential fraudulent activity by assessing anomalies.
As the name suggests, these tools monitor networks to look for unusual patterns or potential breaches. They’re best utilized when trying to identify threats such as malware, phishing, or unauthorized access attempts.
The challenges of risk monitoring
Just as with any high-stakes risk assessment system, risk monitoring is not without its challenges. Here are some of the most common hurdles you might face, as well as ways to overcome them.
Lack of risk awareness
While risk awareness is something which is a top priority for those looking to keep data safe, it’s perhaps not at the forefront of every member of your team (or stakeholders). This can lead to breakdowns in communication, missed deadlines and even inaccurate reporting.
Potential solution
A clear risk management plan that is consistent and has a strong culture. Roles and responsibilities need to be clearly defined, with training on processes, tools, and techniques provided. Regular communication is also a must.
Poor risk identification and analysis
When you lack the time, resources or accurate data to make rounded assessments, you might over or underreact to potential risk factors.
Potential solution
Relying on a diversified set of tools and systems which draw on historical data, expert opinions, market research, or stakeholder feedback. Risk identification and analysis tools are also a must. For that reason, many organizations turn to data management platforms who are experts at assessing risk levels.
Changing risk environments
Internal or external changes to a project can alter risks. This can lead to outdated or irrelevant risk management processes and plans, heightening the chances of unmonitored threats having a negative impact.
Potential solution
A proactive and continuous risk monitoring approach is needed to reduce the impact of a changing risk environment. Audits, reviews and regular reports are key, as well as clear and concise communication internally about any changes to risk.
Poor risk response protocols
Failing to have, or properly follow a risk management strategy reduces the effectiveness of your risk response and mitigation techniques. This can be a drain on money and resources, while also increasing the chances of potential threats having an impact.
Potential solution
A realistic and prioritized risk response plan needs to be created, based on ongoing risk analysis assessments. There needs to be clear ownership for each element of the plan, with ongoing monitoring.
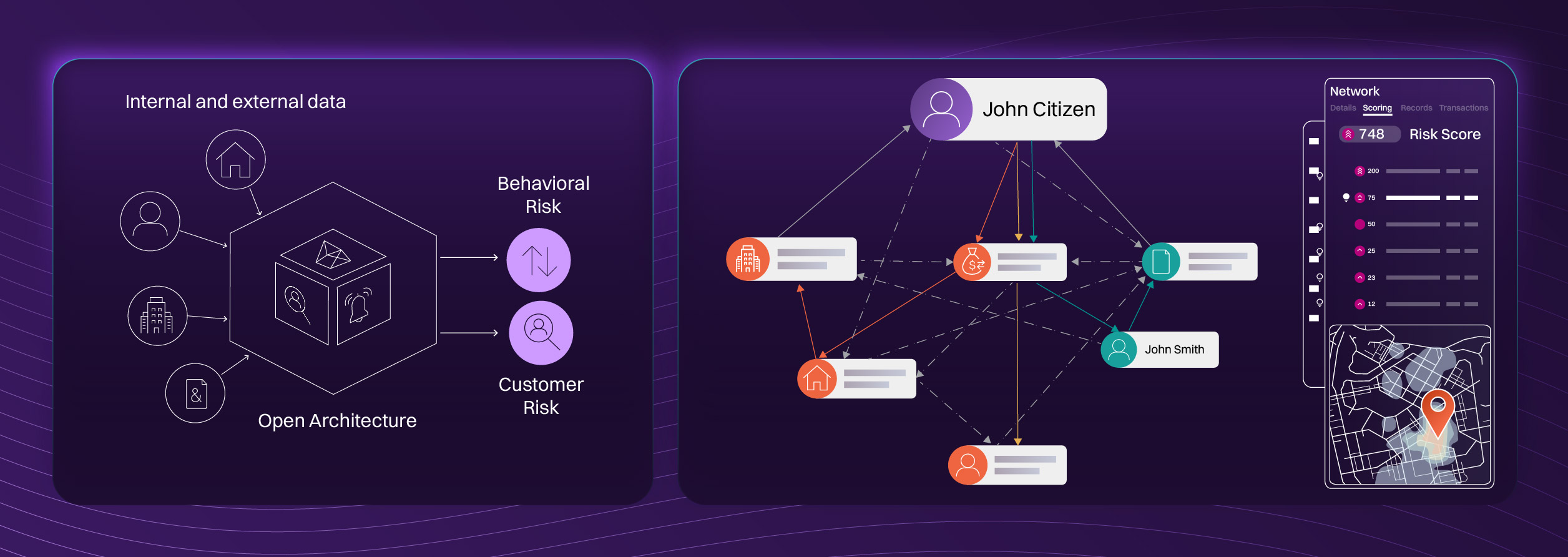
How does Quantexa monitor risk?
At Quantexa, we understand the vital nature of assessing and continuously monitoring risk levels. Our risk management approach aligns lending decisions to enhance resiliency, all while facilitating precise and sustainable lending opportunities for customers. We achieve this by:
Creating 360-views of all parties
We help you understand borrowers and their relationship with other entities, connecting internal and external data to fully assess and understand potential risk points.
Incorporating non-traditional data
External data points can be added to your scoring pipeline to provide a more detailed overview of risk. This helps to inform decision-making when it comes to risk and credit management.
Using Graph Analytics
This detailed analytical system allows you to monitor portfolios and reveal connections which aren’t immediately obvious when using traditional matching approaches.
Using real-time assessment techniques
Early risk warning and signal detection is possible with the use of our credit assessment techniques. These can provide up to 18 months advance warning.
Risk monitoring FAQs
Risk monitoring plays a pivotal role in the continued protection of financial assets and sensitive data. If you’d like to learn more about this intricate system, make sure to read these useful additional queries.
What is an example of monitoring risks?
AML is a good example of a common risk monitoring technique in the world of finance. The ongoing monitoring through specific policies and processes helps to mitigate money laundering and the use of funds for domestic and international terrorism.
What is the difference between risk assessment and risk monitoring?
Risk monitoring is one piece of the wider risk assessment puzzle. Risk assessment is the process of identifying and evaluating potential risks, while risk monitoring is the continuous tracking of known risks to look for changes or detect new and emerging threats.
What is the difference between transaction monitoring and risk monitoring?
Transaction monitoring takes a far more focused look at specific financial transactions, with an aim to identify patterns or anomalies which might indicate illegal activities like money laundering or fraud have taken place. Risk monitoring takes a more holistic approach, assessing an organization’s wider approach to risk compliance and governance. Transaction monitoring can sometimes be a part of wider risk monitoring.
How often should risk monitoring activities be performed?
Ideally, risk monitoring should be an ongoing activity. How regularly you assess a risk will depend on the severity of the risk in question. Lower risks might be monitored monthly or quarterly, while high-risk factors may require real-time monitoring to ensure they aren’t having an impact.
If you’re interested in a rounded approach to risk monitoring, be sure to reach out to a member of the Quantexa team today. We’ll be able to guide you through the most effective ways to monitor risks, ensuring that your organization is kept protected.

